We are in the age of LLMs where everyone wants to use or create LLMs. LLM stands for Large Language Models. There are lots of LLMs available in the market like ChatGPT that everyone uses and other than ChatGPT there are Google’s Gemini, Claude are the LLMs. But everyone uses ChatGPT as it is famous and known to everyone. We all know how to consume these LLMs in only one way i.e. go to an LLM site and search what we want just like google search but we can consume it in a better way by creating applications using these LLMs. You might think about what kind of application we can make using them. How can we create applications by using them? We can create some content creation applications or Chatbots or code generating applications or code analyzing applications. Now in this blog we are creating a RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) application for our personal use which is based on our pdf data. For our RAG application we require LLM model, Embedding Model, Vector DB and some PDFs. For this application we are using Meta’s Llama3 LLM model, Qdrant VectorDB, and Llama Index for Embeddings and Python. You might have some questions like what is a RAG application? What is vectorDB?What is LlamaIndex? And What is Llama3? Let’s see all the above questions one by one.
What is a RAG application?
RAG = DenseVector Retrieval (R) + Incontext Learning (AG)
Retrieval: Finding reference in the document to answer the question asked.
Augmented: Adding some reference to the prompt.
Generation: Improve answers to the asked questions.
So in the RAG application we firstly add pdfs to the vectorDB and then we ask questions based on the pdf and with the help of vectorDB and LLM we get the answer. This is the basic idea behind the RAG application.
What is VectorDB?
VectorDB is just like a regular Database but the key difference is that in our regular database we store data in text or number in row and column format but in vector DB we store data in the vector format. In simple words it is a database which stores data in numerically (vector) format. In out regular RDBMS we retrieve data using SQL query but in the vectorDB as we know now that we store data in form of vector so we can not retrieve data using any type of query we have to search for particular vector to retrieve the particular data from vector store to retrieve particular vector we have to perform similarity search using euclidean distance to understand this concept we take an example Imagine you have a giant library, but instead of books with titles and authors, you have shelves filled with special cards. Each card has a bunch of numbers on it, kind of like a code. These numbers represent the information in a book, like the main ideas and characters.
This special library is like a vector database! It stores information in a way that computers can understand really well, using numbers instead of words.
Regular Libraries vs. Vector Libraries
- Regular Library: You search for books by title, author, or maybe keywords in a catalog. It’s like using a search engine.
- Vector Library: You can’t search by typing words. Instead, you compare the “code” (vector) of what you’re looking for with the codes on the cards. It’s like comparing fingerprints to find a specific person.
Finding the Right Book (Vector) with Similarity Search
Imagine you’re looking for a book about animals. You don’t have a title, but you know there are pictures of animals. Here’s how you might find it in the vector library:
- Create a “Code” for Your Search: You make a special code (vector) based on your idea of “animals.” This could involve things like shapes, colors, and maybe some keywords.
- Compare Codes: The library compares your code with the codes on all the cards.
- Find Similar Books: The library shows you the cards (books) that have codes most similar to yours. These are likely the books about animals you’re looking for!
Why Use a Vector Library?
- Faster Searching: Comparing numbers is quicker than searching words, especially for complex ideas.
- Understanding Similarities: Vector libraries can find things that are similar even if they don’t use the exact same words. Like finding a book about cats even if your code doesn’t have the word “cat.”
What is Embedding?
You might notice above that we are storing text data in the vector database and to store data we need to convert text data into the vector. To do that we use embeddings. Embeddings means the converting text data into the vector form. To understand embeddings let’s continue the above giant library example. Imagine you have a giant library filled with books, but instead of words, each book has a special code made of numbers. This code, called an embedding, captures the main ideas and important parts of the book.
Here’s how it works:
- Words as Building Blocks: Think of each word in a book like a single building block.
- Meaningful Connections: Now, imagine each block has special connections with other blocks based on their meaning. Words like “happy” and “joyful” might be connected because they have similar meanings.
- Capturing the Essence: The embedding process takes all these words and their connections and turns them into a special code (vector) that represents the overall meaning of the book.
Benefits of Embeddings for LLMs:
- Understanding Big Ideas: With embeddings, LLMs don’t need to read every single word in a book. They can understand the main points by looking at the code (vector).
- Finding Similar Books (Information): Just like you can compare fingerprints to find similar people, LLMs can compare embeddings to find information in the library (vector database) that has similar meaning to your question.
So, embeddings are like special codes that capture the essence of information, making it easier for LLMs to understand and work with large amounts of text data!
Now let’s Implement our RAG application
Install Required Libraries
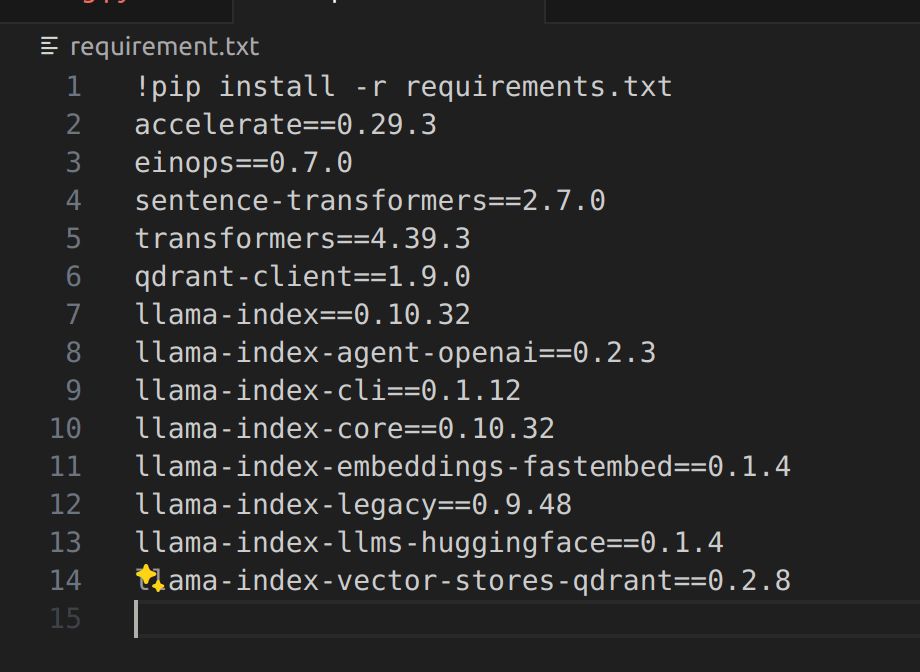
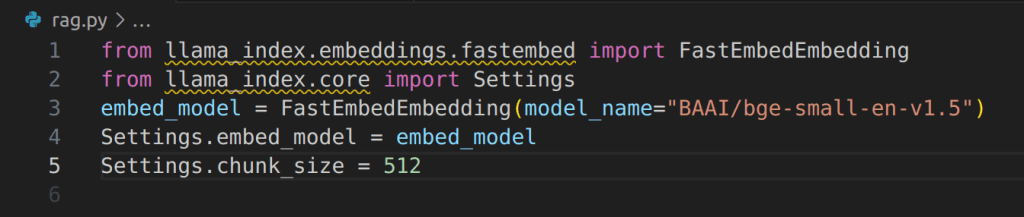
Instantiate the Embedding Model
Define the System Prompt

Instantiate the LLM
Since we are using Llama 3 as the LLM, we need to do the following:
- Generate HuggingFace Access Tokens
- Request access to use the Model
Instantiate the Vector Store and Load the Vector Embeddings
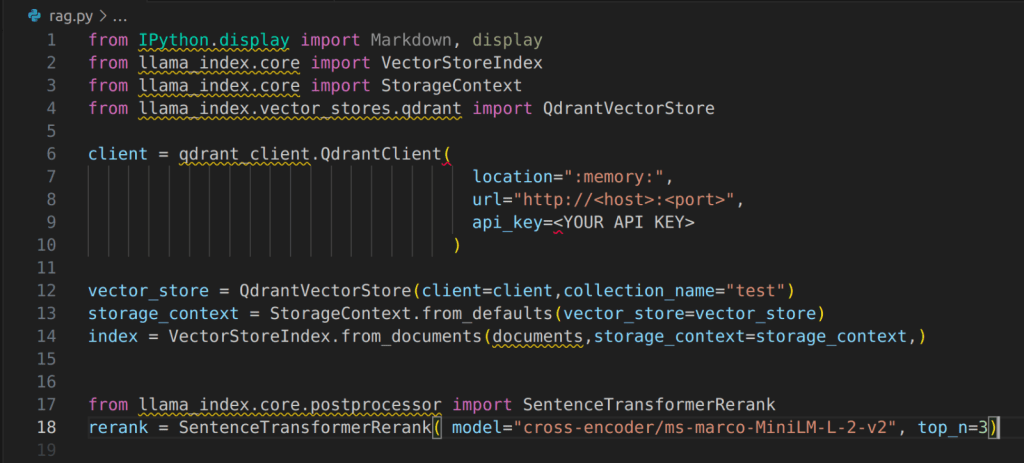
Instantiate the Query Engine

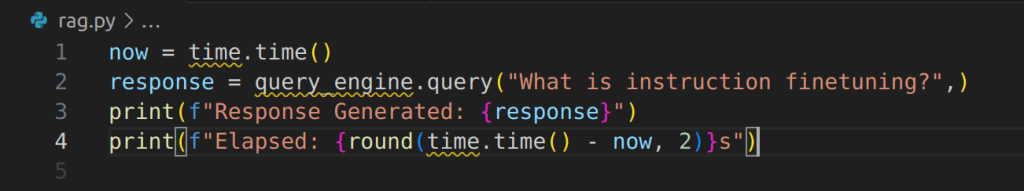
Ask Question
Data
- This application allows you to perform question-answering based on the textual content within your PDFs.
- It works with both public and private PDFs, making it a versatile tool for personal use.
- You can interact with your PDFs in a natural, conversational way, asking questions directly.
Conclusion:
Here we learn about how the RAG application works and how to create our RAG application to chat with pdfs.
We learn about LLMs and Vector databases.


A straightforward guide to building a RAG application for PDF-based question answering using LLMs like Llama 3. Key concepts like VectorDB and embeddings are clearly explained, making it easy to create your own application.
Good Blogs and very Simple explaination, Bro i want the complex maths problem or theories basis on the ML/AI thanks