Welcome to the world of seamless REST service testing with Rest Assured! If you are a developer or automation engineer seeking a reliable solution to validate RESTful APIs, you have come to the right place! Rest Assured is not just another testing tool. It is an open-source Java DSL designed to simplify the testing process while offering the flexibility to write BDD-style scripts for better readability.
In this blog, we shall explore the depths of Rest Assured, exploring its features, capabilities, and how it can revolutionize your testing workflows. But before we dive in, let’s ensure you are set up for success.
To embark on this journey, you will need a few prerequisites in place. First and foremost, make sure you have either Eclipse or IntelliJ installed on your system. These powerful IDEs will serve as our playground for crafting and executing tests with ease.
Next up, let’s set up our project structure. We will be using Maven as our project management tool. So, fire up your terminal and create a new Maven project using the “maven-archetype-quickstart” from the Apache repository. This will lay down the foundation for our testing environment, ensuring we have everything we need to get started.
With our prerequisites in order and our project structure established, we are ready to explore the ins and outs of Rest Assured and how it seamlessly integrates into your CI/CD pipelines.
Adding Maven Dependencies to the POM File
To ensure smooth integration and functionality within our project, we need to include specific Maven dependencies in our pom.xml file. These dependencies will provide us with the necessary tools and libraries to effectively utilize Rest Assured and streamline our testing processes. Let’s take a look at the required dependencies and make sure to update them with the latest versions.
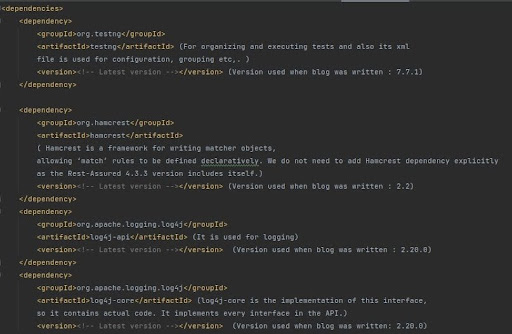
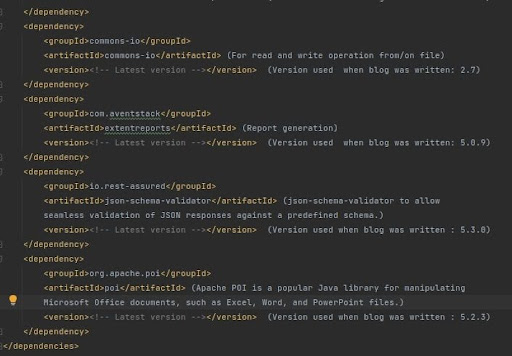
Make sure to replace <!– Latest version –> with the most recent versions of the respective dependencies available at the time of your project setup. Keeping these dependencies up-to-date ensures compatibility with the latest features and enhancements, contributing to a robust testing environment.
- Examples of Basic CRUD Operations
In our exploration of Rest Assured, let’s dive into some practical examples of CRUD operations. These examples will showcase how Rest Assured simplifies the process of testing RESTful APIs. We will cover the basic CRUD operations: Create, Get, Update, and Delete. You can refer to the Postman documentation
- Understanding Basic Functions and Keywords in Rest Assured
Before we delve into examples, let’s familiarize ourselves with some fundamental functions and keywords used in testing APIs with Rest Assured:
- Given: Input details such as path parameters, query parameters, headers, and request body.
- When: Method used (GET, PUT, POST, PATCH, DELETE, UPDATE) and resource URL.
- Then: Assertions and validations.
Keywords:
- extract(): Extracts API response details once the API is triggered.
- assertThat().statusCode(): Asserts the status code.
- response(): Fetches the response.
- asString(): Converts JSON response to a string.
- auth(): Adds authentication if required.
- basic(): Provides basic authentication with username and password.
- JsonPath: JsonPath is used to parse and query JSON.
Now, let’s put these concepts into action with some CRUD examples using Rest Assured. Stay tuned as we walk through each operation, demonstrating the simplicity and power of Rest Assured in action.
- Implementing Basic CRUD Operations with Rest Assured in Java
In this section, we will walk you through the implementation of basic CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations using Rest Assured in Java.
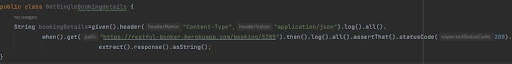
- GET Method – Fetching Booking Details
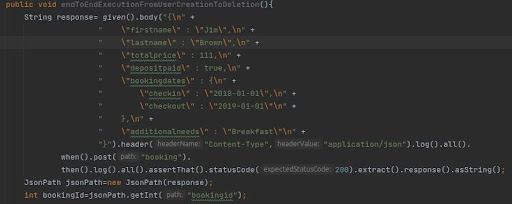
- POST Method – Creating Bookings
- Request Body in the Test Case Itself
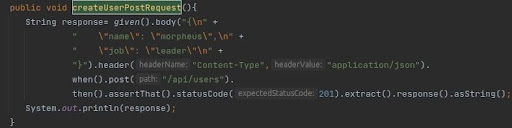
- Sending Hard Coded Static Request Body as a variable
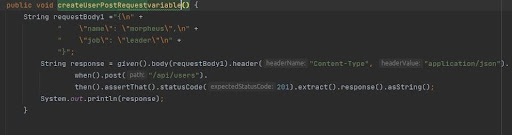
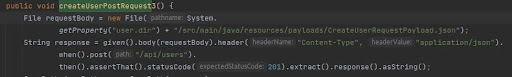
- Sending Static JSON File in the Request Body
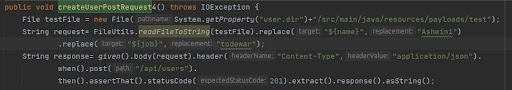
- Sending Text File with a Variable Declared which will get replaced at runtime
- Exploring Different Approaches for Sending JSON in a POST Request:
- Sending the Request Body Directly Within the Test Case and as a variable:
- This approach involves directly embedding the JSON request body within the test case code itself.
- It is suitable for scenarios where the request body is relatively simple and does not require frequent changes.
- Storing Static JSON in a File and Sending it as Part of the Request:
- In this method, the JSON payload is stored in a separate file and then read and sent as part of the request.
- It offers better maintainability, especially when dealing with large or complex JSON payloads that may need frequent updates.
- Utilizing Dynamic JSON with Variables Inserted for Each Field:
- Dynamic JSON involves creating JSON payloads with placeholders for variables that are replaced with actual values during runtime.
- This approach offers flexibility and reusability, allowing for easy customization of request bodies based on different scenarios or test data.
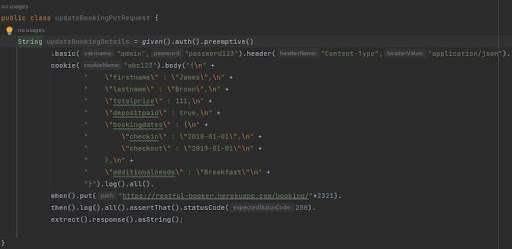
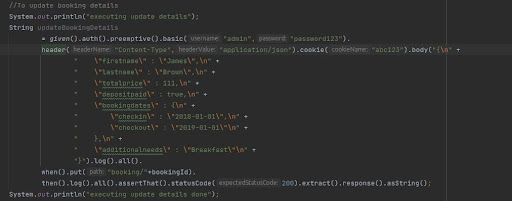
- PUT Method – Updating Booking Details
- DELETE Method – Deleting Bookings
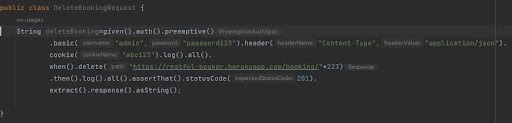
- End-to-End Execution with API Chaining
API chaining, also known as end-to-end execution, involves orchestrating a sequence of API calls where the output of one API request serves as the input for the next. This technique streamlines the execution of multi-step processes in an automated manner.
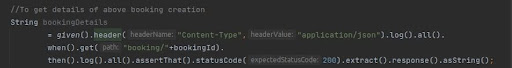
To get details of the above booking creation ( Booking Id from above POST api call is
getting used in fetching newly created booking ID and check Successful creation of booking )
To update booking details (The same booking ID is getting used to change the existing
content using PUT method )
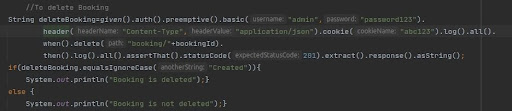
To delete the Booking (Same Booking ID is getting used to delete booking )
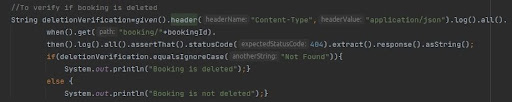
To verify if the booking has been deleted
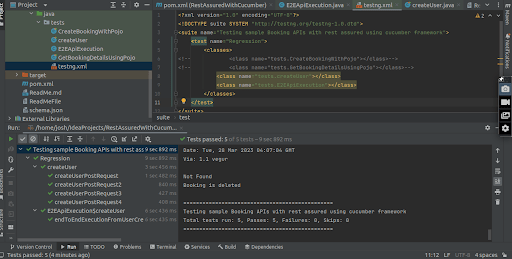
Test Run Result:
After implementing the CRUD operations using Rest Assured with Java, a test run was conducted to validate the functionality. The results of the test run are as follows:
Git Repo URL:
https://github.com/ashwinitodewar491/RestAssuredWithCucumberFramework
References:
- For Fetching Maven dependencies please use the following link and on the search bar enter the dependency name
https://mvnrepository.com/ - We can use https://jsonpathfinder.com/ to cross-verify the path of the JSON response while adding an assertion.
- Sample API testing sites:

